Información legal:
Titular de la página web: Gris Reproducción SL
Propiedad Intelectual:
Todos los derechos de explotación están reservados. Queda prohibida la reproducción, retransmisión, copia, ce-sión o difusión total o parcial de su contenido sin autorización expresa y por escrito. Tampoco se autoriza:
- La PRESENTATION de una página del sitio web en una ventana que no pertenezca a Gris Reproducción SL por medio de "framing".
- La inserción de una imagen difundida en el sitio web en una página que no sea de Gris Reproducción SL mediante "in line linking".
- La extracción de elementos del sitio web causando perjuicio a Gris Reproducción SL, de conformidad con las disposiciones vigentes.
Garantías y Responsabilidades:
Gris Reproducción SL no asume la responsabilidad de las infracciones en que puedan incurrir los usuarios ni de los daños y perjuicios causados por la utilización de esta web, y se reserva el derecho de actualización y modificación de la información sin previo aviso.
Gris Reproducción SL no asume la responsabilidad del contenido, la veracidad y los errores en los enlaces a los que se puede acceder a través de la página web. La única finalidad de los enlaces consiste en proporcionar a los usuarios el acceso a una información que pueda ser de su interés.
Las anteriores condiciones se regirán por la normativa española.
08017 - Barcelona - Spain
Telephone: (+34) 93 280 65 35
Fax: (+34) 93 280 08 71
doctorgris@doctorgris.com

The in vitro fertilization is a procedure that allows fertilization of the female egg by a sperm in the laboratory and not in the uterine tube.
IVF is indicated in the following cases:
- No tubes or tube injury
- Age of women
- Endometriosis
- Immunological Causes (semen, cervix)
- Cause unknown (idiopathic)
- Men's severe
- No success in artificial insemination
- Donations oocytes (Early Ovarian Failure in receiving)
- Cancer Therapy (freezing of embryos prior to chemotherapy).
There are two techniques:
- The classical IVF in which eggs are extracted from the ovaries of women and placed in an incubator stove with the sperm of the couple.
see photos
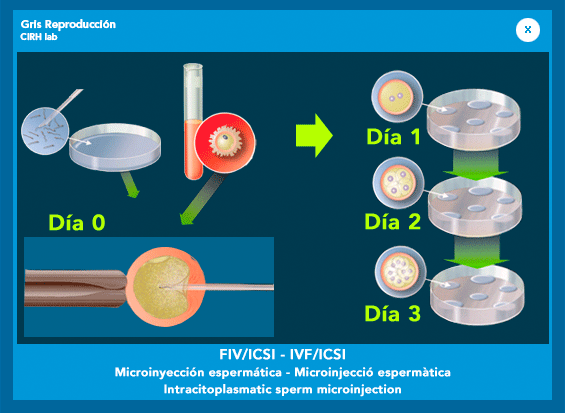
- The IVF/ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm microinjection), which consists of introducing a single sperm into the interior of each egg.
see photos
Stages of IVF treatment
1. Ovarian stimulation: There are several types of ovarian stimulation protocols. They are generally referred to as "long” or agonists protocol and “short” or antagonists protocol. There is a protocol with short-agonists that are obsolete by the poor results that are achieved with this.
In the protocol "long-agonists”, a drug called analogue agonist was initially administered. This medicine may be administered via intranasal or subcutaneous. It is always initiated in the second half of the menstrual cycle (luteal phase), approximately in the 21st cycle day. After the 10-14 days of starting treatment, the patient has the menstruation. At the moment we perform an ultrasound control and a blood test (estradiol determination).
The objective of this part of treatment is to get that one of the organs involved in ovulation, the pituitary, did not trigger the secretion of a hormone (LH) and, therefore, the ovulation; before getting the proper development and maturation the ovarian follicles, which contain the ova.
If the ultrasound control and the analytical determination of estradiol found that there has been desensitization of the pituitary, we can start treating ovarian stimulation.
The stimulation of the ovaries is performed with subcutaneous injections. Sometimes it is advisable to combine the administration of two different types of injections to the correct follicular development. The right Follicular development is proportional to the proper maturation oocyte. We wouldn’t achieve fertilization of egg by sperm, without the removal of part of its genetic material (meiosis). Ova and sperm have half the number of chromosomes (23) than any other somatic cell of our bodies (46 chromosomes).
During the stimulation of the ovaries ultrasound inspections and a test of estradiol are accompanied per visit.
When we get follicles in the size of between 17 and 22 mm, another injection should be given (HCG) to release the egg inside the follicle and complete the maturation of that.
The protocol "short or antagonists” starts the day after menstruation. The ovaries are stimulated with subcutaneous injections for 5 or 6 days. At this moment, we perform the first ultrasound control and estradiol determination in blood. From this moment we start treatment with other subcutaneous medicines (the antagonist). This helps us to avoid the peak of ovulation triggered by the pituitary gland (LH). Now, the treatment goes in a similar way as we explained in the preceding paragraph.
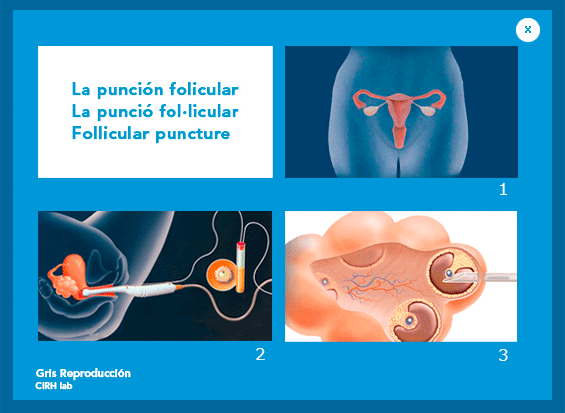
2. Follicular puncture: This will be done 36 hours after the HCG injection. At present the aspiration of the eggs are performed via puncture of the ovaries and aspiration of the follicular fluid, continuously controlled by vaginal ultrasound, under general anesthesia in the operating room. At this moment the couple is requested to obtain a sample of sperm. see photos
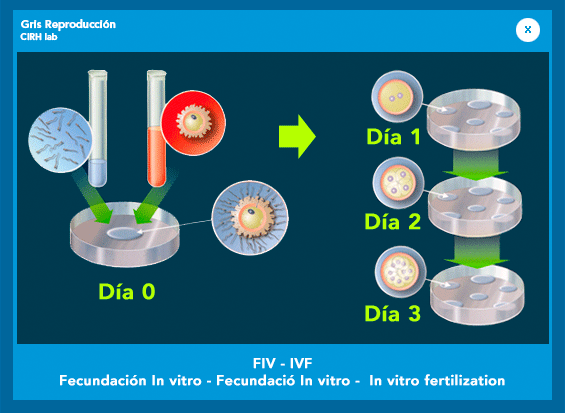
3. Fertilization in the laboratory:After obtaining the oocytes, laboratory work begins in which biologists will try to get the union of oocyte cells extracted from the patient with sperm from the couple.
It is at this stage of the treatment when we can apply another technique: la intracytoplasmic sperm injection ICSI, which consists of introducing a sperm in each oocyte.
The whole process of fertilization occurs about 18 hours after the insemination of the egg, and approximately 12 hours after the fertilized oocytes or pre-embryos begins the process of cell division. Once the embryologist suggests that the embryos are in a suitable state, proceed to transfer them into the uterus. Usually the transfers are done 2 or 3 days after the follicular puncture.
4. Embryo transfer: The transfer is the introduction of the embryos in the uterus of the patient, using a thin tube that is inserted through the cervix. We consider this event of great importance. We perform it by direct control provided by ultrasound, which allows the gynecologist a control at every moment where he must deposit the embryos. It is a simple and painless process, which does not require anesthesia. see photos
The preparation requires: 1.Treatment with progesterone from the day of the puncture, 2. A degree of filling of the bladder (feeling the need to urinate) in order to control the ultrasound that is done during the transfer of embryos.
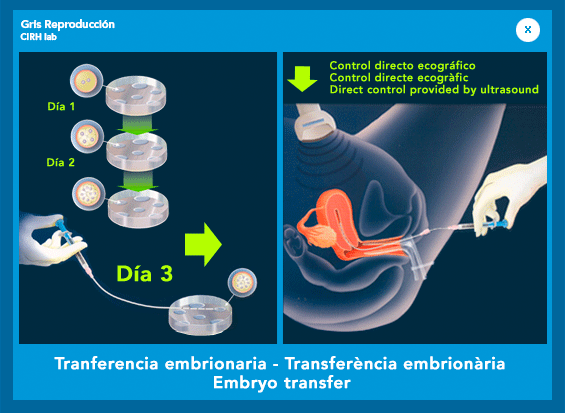
Our couples, if they wish, they can see their embryos at the time prior to the transfer via a closed circuit TV that provides them with images from the laboratory.
On the day of the transfer biologists will evaluate the status of embryos and guide patients in the decision to transfer one, two or three embryos (the current Spanish law on Assisted Reproduction does not allow more than three embryos transferred in each cycle). If we get more viable embryos than we have transferred, they will be frozen and may be used in possible future cycles -cryotransfer -.
The pregnancy test should be performed on blood twelve days after the transfer, through analysis of the hormone beta-HCG. This hormone is present in pregnant women. If the test is being performed on urine, as the concentration of the hormone twelve days after the transfer is too low, it could be negative.
pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
This technique allows the study of some chromosomes of embryos obtained in the laboratory.
Patients area | First visit | Diagnostic tests | Psychological support | How to visit | Frequently asked questions | Oocyte donation | Sperm donation |
Documents | News | Legal notice | Credits: Deumonforte